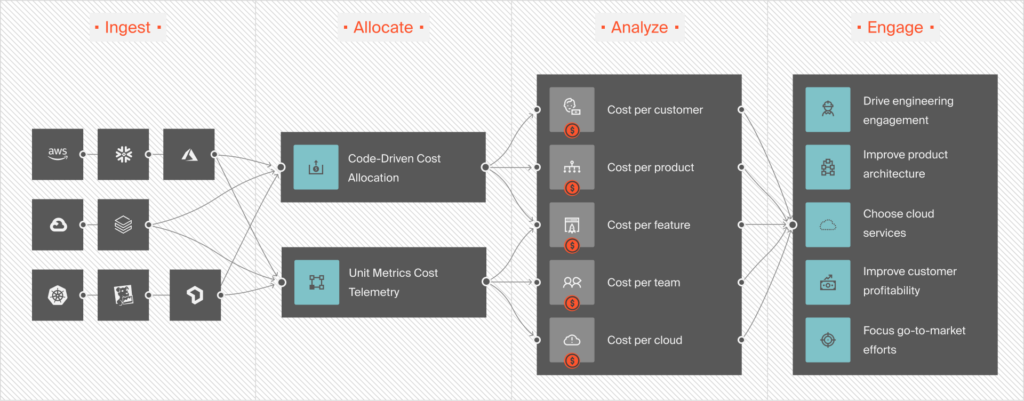
Inside this article :
To fully capitalize on the advantages of cloud technology, businesses need a well-planned, thoughtful approach. The cloud offers immense flexibility, scalability, and innovation potential, which can quickly become a financial burden if not managed correctly.
Due to a lack of proper planning and resource management, many companies mistakenly believe that simply adopting the cloud guarantees cost efficiency, only to face unexpected bills and uncontrolled expenses. This is where cloud cost optimization comes in. It’s strategically managing cloud resources to maximize value while minimizing unnecessary spending. This guide will walk you through the fundamentals of cloud cost optimization, providing the essential tools, strategies, and techniques to help streamline your cloud usage and ensure you’re getting the most out of your investment.
So let’s dive in.
What is Cloud Cost Optimization?
Cloud cost optimization is managing cloud spending by cutting waste, right-sized services, and enhancing providers’ discounts. The ultimate goal is to minimize costs by maintaining performance and scalability by effectively using resources.
For many businesses, it means reducing unnecessary spending and gaining more capital for growth. For instance, a Saas company can schedule AWS instances to shut down during off-peak hours to save money without sacrificing productivity.
What is the Role of Cloud Cost Drivers in Cloud Cost Optimizations?
Cloud costs are driven by computing storage and networking, which are essential in cloud cost optimization. Compute, storage, and networking are the primary services that drive cloud cost. These services usually come with variable cost structures based on usage, location, and type of deployment that directly impact overall cloud expenses.
Key Factors Affecting Cloud Cost
- Idle resources still cost expenses, leading to unnecessary expenses.
- Allocating excessive resources leads to inflated costs without delivering proportional values.
- Mismanagement of reserved instances typically results in a loss of long-term savings.
- Cloud service pricing model- pay-as-you-go is considered optimal for fluctuating workloads.
Strategies for Cloud Cost Optimization
Cloud cost optimization needs a combination of technology and strategic planning. By implementing efficient strategies, businesses can reduce expenses and maintain high performance in their cloud environments.
1. Using Cloud Provider Cost Management Services
Cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer built-in cost management services (e.g., AWS Cost ExplorerAzure Cost Management) to help businesses manage their cloud expenses. These services track real-time usage, forecast costs, and allow businesses to set budgets. Plus, by using these tools, companies can gain insights into their spending patterns and make data-driven decisions to control costs and avoid overspending.
2. Implementing Storage Lifecycle Policies
Businesses can move data from high-cost storage to lower-cost archival solutions by setting up automated storage lifecycle policies. Frequently accessed data stays on faster, more expensive storage, and less-used data is shifted to cheaper, long-term storage, minimizing costs without sacrificing accessibility.
3. Adopting a FinOps Culture
FinOps brings together teams across finance, operations, and engineering to optimize cloud spending. Companies can manage costs effectively by supporting innovation and growth, by tracking cloud usage in real time and promoting collaboration.
4. Utilizing Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for Cost Management
IaC tools like Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, ARM and Google Cloud Deployment Manager automates cloud infrastructure management. It allows for automating tasks like resource shutdown during off-peak hours or removing unused resources, by helping companies prevent unnecessary costs and improve overall efficiency.
5. Multi-Cloud Deployment for Service Availability
A multi-cloud approach involves utilizing various cloud providers (e.g., AWS, Azure, GCP) for high availability, reduce dependency on a single provider, and improve fault tolerance. These strategies increases service continuity and allows businesses to take advantage of the unique strengths and capabilities of different cloud platforms, while also mitigating risks associated with provider outages.
6. Using Spot Instances for Cost Savings in Non-Critical Environments
Spot instances offer significant discounts on cloud resources by leveraging unused capacity. It makes them ideal for non-critical tasks such as data analysis, batch processing, or rendering. By using spot instances, businesses can significantly reduce their cloud infrastructure costs while mission-critical workloads remain on more stable, on-demand instances.
7. Network Cost Optimization Using Traffic Shaping
Managing data transfer between cloud regions can be costly. Traffic shaping techniques optimize data flow to reduce unnecessary transfers by cutting down on high inter-region fees. They are generally useful for businesses with heavy data transfer needs.
8. Cloud-Native Re-Architecture
Re-architecting applications with a cloud-native approach utilizes managed services, serverless options, and regionalized resources. It can optimize performance and reduce costs. This design minimizes cross-region data transfers, making it ideal for businesses with high data transfer needs. It maximizes resource use and enhances scalability within the cloud.
9. Task Scheduling to Avoid Peak Hours
During price spikes, cloud providers go through peak demand periods. Businesses can reduce costs without affecting the complete time of long-term processes by scheduling tasks to run during off-peak hours when cloud resources are available. It works especially well for jobs that are not time-bound but need the tasks to be completed within the defined timeframe.
What are the Most Essential Tools for Cloud Cost Optimization
Cloud cost optimization depends upon the right tools to gain visibility into total spending and implement cost-saving strategies. However, native and third-party tools equally help in acquiring control over cloud costs.
1. AWS Cost Explorer
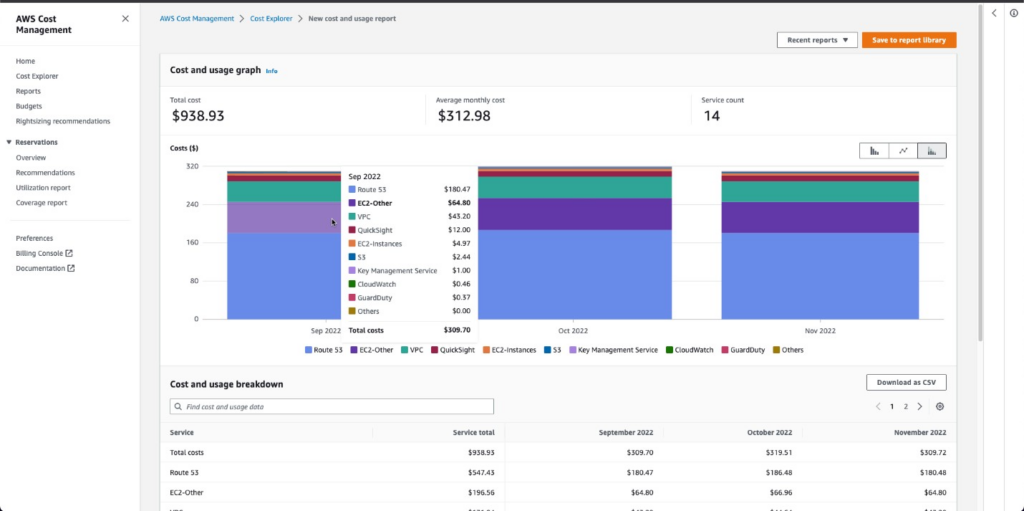
- It provides detailed insights into AWS spending patterns.
- It helps businesses track, report, and optimise costs within the AWS environment.
- Offers a comprehensive view of AWS-specific usage.
2. Azure Cost Management + Billing
- This tool includes budgeting and cost analysis features for Azure users.
- It offers clear visibility into cloud spending within the Azure ecosystem.
- This cost management tool is effective for Azure users but needs multi-cloud visibility.
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Pricing Calculator
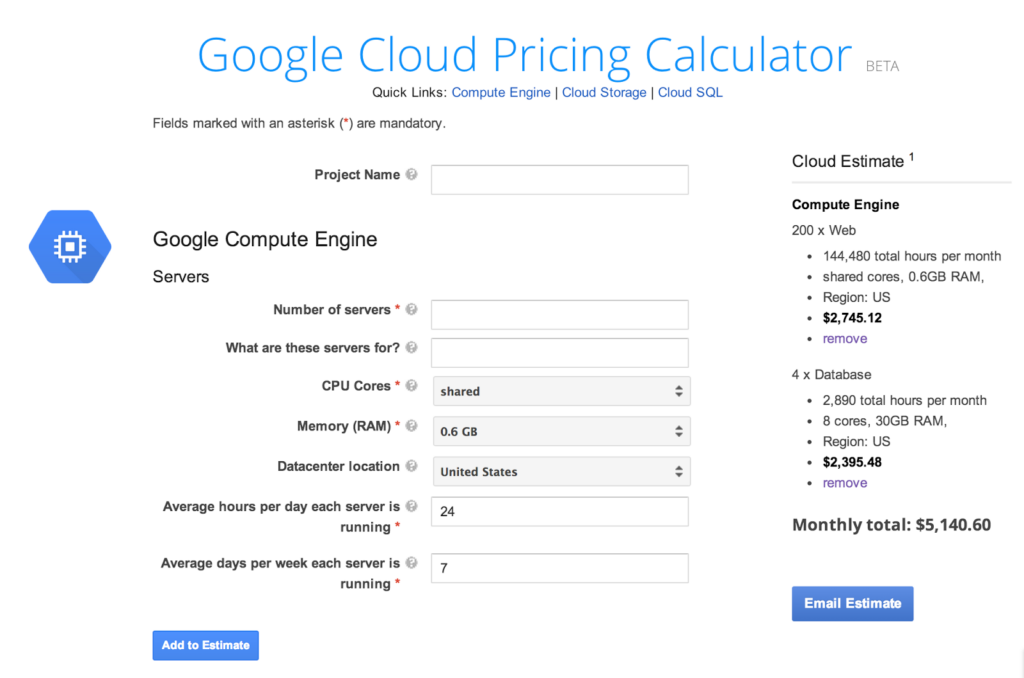
- GCP helps estimate costs before deploying resources.
- It navigates the planning of cloud infrastructure spending effectively.
- It is used for a single cloud.
4. Third-Party Tools: CloudZero, Spot.io, Densify, Antimetal, Amnic
- They provide multi-cloud visibility that allows businesses to manage costs across various cloud platforms.
- These tools offer predictive analysis and cross-cloud cost management.
- They are Ideal for businesses with complex, multi-cloud environments requiring advanced cost control solutions.
Integrating cloud cost optimization tools, whether unified or third-party, into DevOps workflow helps businesses monitor cloud spending, set up automated alerts, and make real-time adjustments to optimize cloud cost on all platforms.
Next, we will learn about best practices for cloud cost optimization that are important to initiate cloud cost optimization.
Best Practices for Cloud Cost Optimization
Businesses need to implement proactive and strategic practices to manage cloud costs effectively. These best practices check cloud usage is aligned with financial goals by maximizing operational efficiency.
1. Proactive Monitoring and Cost Management
Dashboard setup and automated reports help businesses to have a close eye on cloud usage and costs. Moreover, teams can quickly adjust to avoid budget overruns by identifying the spending trends and potential waste areas. Real-time monitoring offers transparency and allows for rapid responses when unusual cost spikes take place.
2. Setting Up Budgets and Alerts
Cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer built-in tools to set budgets and cost alerts. Once the cloud threshold is established, businesses can be notified when spending approaches or exceeds limits. This early warning system lets organizations mitigate unexpected costs and make accurate decisions before expenses get out of control.
3. Continuous Rightsizing and Optimization
Businesses sometimes allocate more storage or computing resources than they actually need, thinking it will prevent performance issues. Rightsizing includes adjusting these resources to fit actual usage to ensure efficiency and reduce overspending. Optimization techniques include auto-scaling, which allows resources to increase or decrease as demand fluctuates.
4. Using Tags for Better Cost Allocation
Resource tagging lets businesses allocate cloud costs more precisely across various departments, projects, or teams. By tagging cloud resources, companies can track which team uses specific resources, enabling better financial accountability. It improves budgeting and allows each department to be responsible for cloud consumption.
5. Encouraging a Cloud-Cost-Conscious Culture Within Teams
Cloud optimization is not just an IT responsibility but requires a broad company mindset. If employees are encouraged to adopt a cloud cost-conscious culture, everyone will be mindful of how their decisions impact the company’s cloud bills. In this case, regular training sessions, internal policies, and cost-saving tools become part of daily operations to reinforce awareness.
6. Collaborating Between IT, Finance, and Development Teams
Cloud cost management requires collaboration between IT firms, finance, and development teams. IT firms make the infrastructure run effectively, finance tracks the costs, and development teams check on the resources utilized effectively. By aligning this goal, the company maximizes cloud usage without overspending, which leads to better decisions regarding cloud investment.
7. Automated resource scheduling
Many businesses leave non-critical resources running 24/7, which leads to unnecessary expenses. The start and stop time when automated, especially for development, testing, and non-peak workloads, businesses can reduce idle costs by maintaining productivity. Automation tools schedule resources for you to pay for what you use.
Advanced Cloud Cost Optimization Techniques
Businesses take cloud cost savings to the next level by implementing advanced optimization techniques. These cloud cost optimization techniques cut down unnecessary spending and ensure that cloud resources are used at their full potential.

1. Function-level Billing Audits
In serverless architectures, costs accumulate and go unnoticed at a functional level. However, regular audits of individual functions, such as AWS Lambda or Azure, help identify and eliminate underused or redundant services. It makes sure that you are paying for the computing power you paid.
2. Cold-start Penalty Reduction in Serverless
In serverless environments, inefficient function execution can lead to cold starts, which cause delays and drive up costs. Due to infrequent function usage or poor optimization, cold starts happen when the serverless platform needs to initialize resources to handle incoming requests. It not only increases response times but also incurs extra costs, especially if functions are frequently triggered without being optimized to reduce these initialization delays.
3. Custom Routes to Optimize Network Egress
Network egress, or data transfer charges, is integral to cloud expenses. Businesses can reduce egress costs and improve efficiency by creating custom network routes. It helps minimize traffic through expensive paths and avoid unnecessary cross-region transfers.
4. Using Containers for Cost Efficiency in Cloud-Native Environment
Containers are a core component of the cloud-native approach. It makes better resource utilization by running multiple applications or services on shared infrastructure. This approach reduces the need for separate virtual machines by making cloud resources effectively distributed and scalable. By using containers, businesses can optimize cloud resource usage, which allows for better scaling and significantly lower costs.
5. Commit to Reserved Instances or Savings Plans
For predictable workloads, Reserved Instances or Savings Plans on AWS or Azure offer up to 70% savings over pay-as-you-go. Using AMD-based instances or AWS Graviton processors can further reduce costs, which makes this approach ideal for steady and continuous operations.
6. Automate resource scheduling to eliminate idle costs
Many organizations leave non-essential resources running 24/7, raising idle costs. If these resources’ start and stop times are automated in the development and testing environment, businesses can reduce waste and ensure resources are only active when needed.
7. Design cost-aware architecture to maximize resource efficiency
The cloud environment is designed with cost efficiency as a priority. It includes optimizing storage tiers, using scalable architecture and deploying microservices wherever required. Developing cost-aware applications helps businesses to extract maximum performance without unnecessary expenditure.
How Cloud Pricing Models May Evolve Shortly?
As cloud adoption increases, pricing models will become more flexible, transparent, and tailored to business needs. Let’s discuss a few trends that may shape the future of cloud pricing:
1. AI-driven Cost Prediction
Cloud providers can use AI and ML to predict future costs based on usage patterns and projects. It allows businesses to optimize resource allocation and avoid unexpected cost spikes.
2. Tiered and Dynamic Pricing for Data Storage
Data storage and transfer pricing could become more dynamic, with the cost varying by data type, access frequency, and region. Off-peak discounts encourage cost savings.
3. Flat-Rate and Subscription Models for SaaS/PaaS
Predictable subscription models will become more common for SaaS and PaaS services. It will offer businesses more control over budgeting with bundled discounts for long-term commitments.
4. Sustainability Linked Pricing
Eco-friendly pricing can reward businesses using energy-efficient cloud resources or renewable energy-powered data centres.
5. Edge and IoT-Specific Pricing
Specific edge computing and IoT pricing may minimize distributed, real-time processing costs and lower cloud egress charges.
6. Marketplace and partner-driven discounts
Cloud providers can offer bulk discounts for businesses using third-party services by integrating costs across multiple platforms for more streamlined billing.
7. Custom hybrid cloud pricing
Businesses can gain more flexibility to shift resources between public and private clouds with unified billings and discounts across multiple platforms.
Maximizing Efficiency, Savings, and Sustainability in Cloud Environments
To truly maximize efficiency, savings, and sustainability in the cloud, businesses must adopt a proactive approach to cost management. Cloud cost optimization isn’t just about reducing expenses—it’s about making smarter decisions that align with business goals while minimizing environmental impact.
Regularly reviewing resource allocation, automating processes, and balancing pay-as-you-go with long-term savings contribute to a lean, cost-effective, and eco-friendly cloud environment. At Stackgenie, we deliver cloud cost optimization strategies tailored to your needs. Our expertise lets you streamline your cloud operations and expands substantial savings by maintaining peak performance. Contact us today to learn how we can help you optimize your cloud costs and achieve peak efficiency!
FAQs
1. How often should companies review their cloud costs?
Companies should review their cloud costs monthly, but if they want more frequent reviews, they can do them weekly to learn the business’s rapid usage patterns. Regular reviewing helps detect anomalies, prevents over-provisioning, and adjusts resource allocation to align with business and operational needs.
2. Can small businesses benefit from cloud cost optimization strategies?
Yes, of course, small businesses can significantly benefit from cloud cost optimization strategies. Unnecessary expenses can be reduced by rightsizing resources, setting budgets and alerts, and using automation tools; small firms can reduce unnecessary costs and improve the cloud environment that allows them to compete more effectively.
3. What are some unique indicators of wasteful spending in cloud environments that organizations often overlook?
Some overlooked indicators of wasteful spending are underutilized resources, unnecessary backups, redundant data storage and unmonitored SaaS subscriptions. Companies even overlook orphaned resources like unattached storage volumes or unused IP addresses that may still generate costs.
4. What innovative approaches are organizations taking to manage cross-cloud costs?
Organizations are adopting multi-cloud management platforms that offer primary control over cloud usage across different providers. Many are AI-driven analytics tools that can predict future costs and automate resource allocation based on usage trends. Another innovative approach is consolidating billing and leveraging partner-driven pricing for more choice rates across cloud providers.
5. What are the risks associated with over-optimizing cloud costs?
Over-optimizing Cloud costs lead to risks like under-provisioning, which can result in poor performance, service outages, and delays. It can also negatively impact user experience and business operations. Balancing cost optimization with performance requirements is the answer to avoid these risks.
6. What is the role of FinOps in cloud cost optimization?
FinOps helps optimize cloud costs by bringing together finance, tech, and business teams to manage spending efficiently. It provides real-time visibility, aligns financial goals with operations, and enables data-driven decisions. FinOps helps identify inefficiencies, optimize resource allocation, and ensure cost control while supporting business growth along with establishing accountability and tracking expenses.